OCR Text Extraction From Student Card
Project Background & Description
Click here to visit github repo
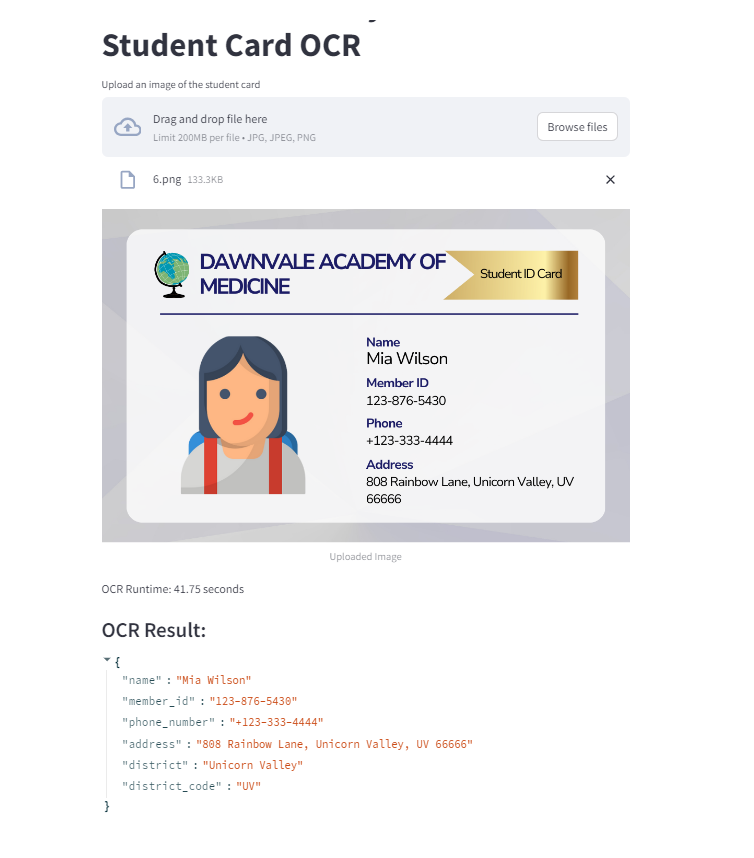
Our Student Card Scanner is a smart tool designed for a fictitious educational institution, Dawnvale Academy of Medicine (dummy data was made using Canva)
Key Features:
- Corner Detection: the scanner spots the corners of the card and adjust orientation if needed
- OCR: it scans ID cards and converts into text
- Data Extraction: it retrieves important details from scanned ID cards such as names, ID numbers, addresses, and phone numbers. Including double-check district info we extract by comparing it to master data and return the closest match from the list
Plus, we’ve wrapped it all in a API and a Streamlit interface for demo
Corner Detection
- Data Preparation
- Gather student card images, including rotated variations
- Labeling with LabelIMG
- Annotate corner points on images using LabelIMG
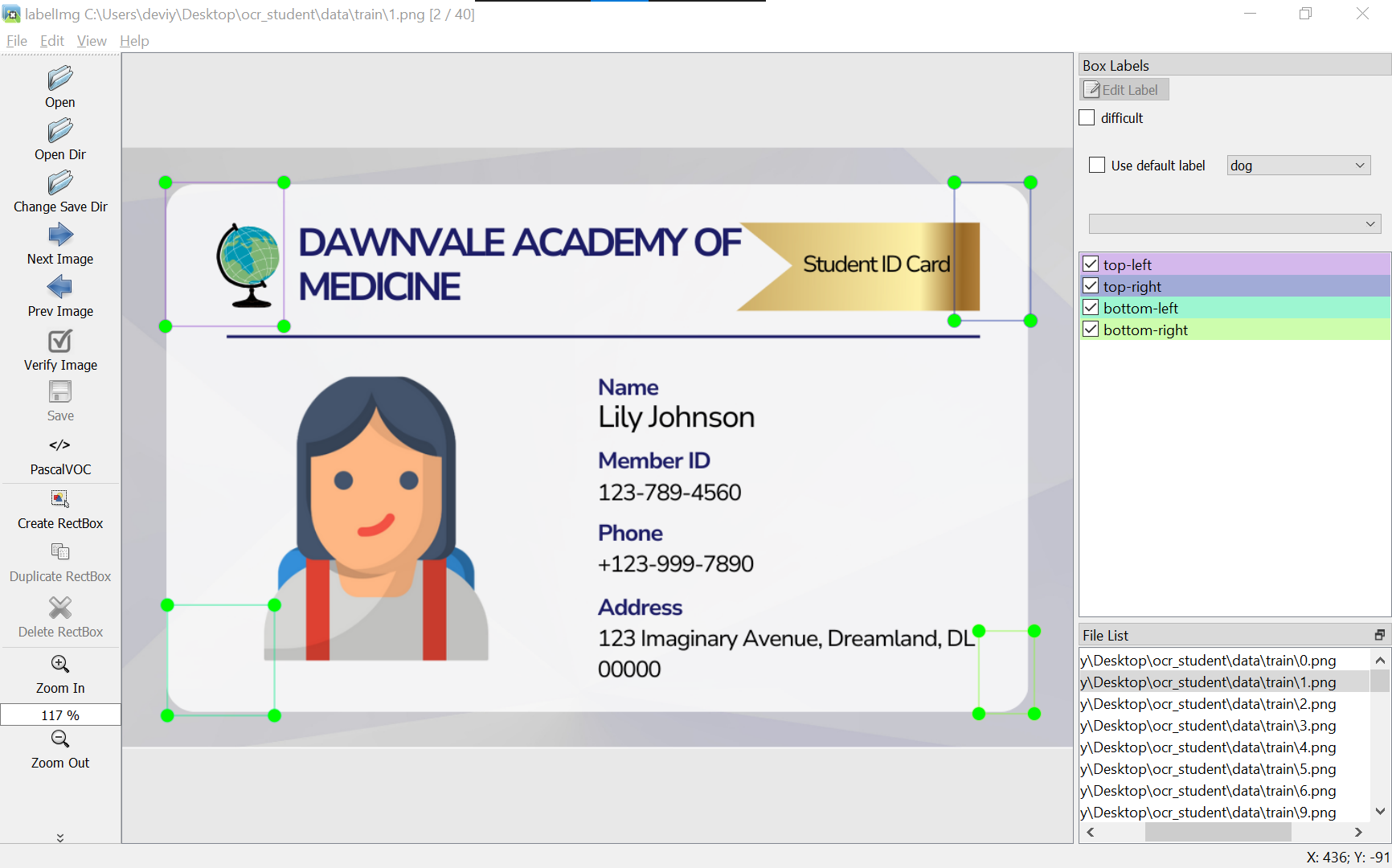
- Annotate corner points on images using LabelIMG
- Convert to COCO Format
- Convert annotated dataset from Pascal VOC to COCO format for Detectron2 compatibility
- Training
- Train Detectron2 with the converted dataset (10 images).
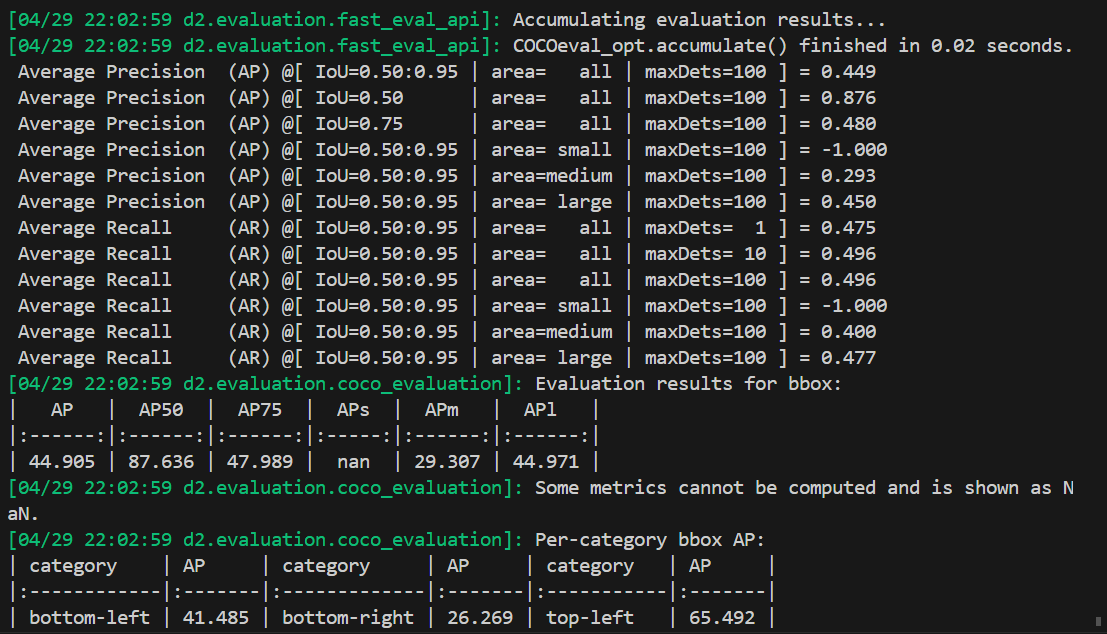
- Train Detectron2 with the converted dataset (10 images).
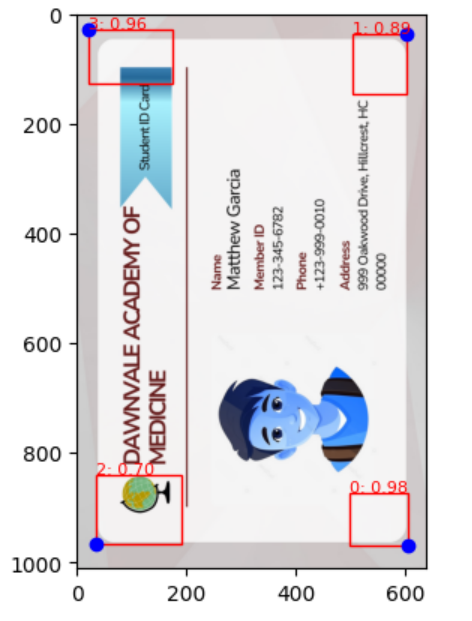
- Predict
- predict corner detection on test data
- predict corner detection on test data
To note: Our Detectron2 model for student card corner detection was trained one time due to resource constraints (CPU only). Although initial performance may be suboptimal, we improved accuracy by addressing duplicated output in subsequent OCR tasks.
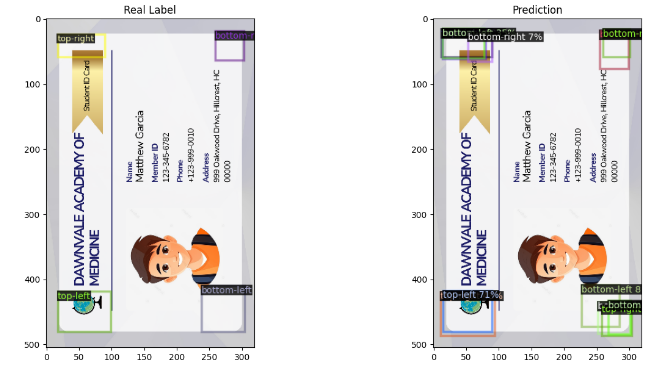
- Duplication Correction
- Address duplicated output in OCR tasks to enhance model accuracy
- Address duplicated output in OCR tasks to enhance model accuracy
- Reorientation or Crop if Needed:
- Utilize corner detection results to reorient or crop images as necessary for further processing


- Utilize corner detection results to reorient or crop images as necessary for further processing
OCR
- Prepare Data
- Utilize the EasyOCR available model, to convert images to text and generate cropped images. Relabel if needed
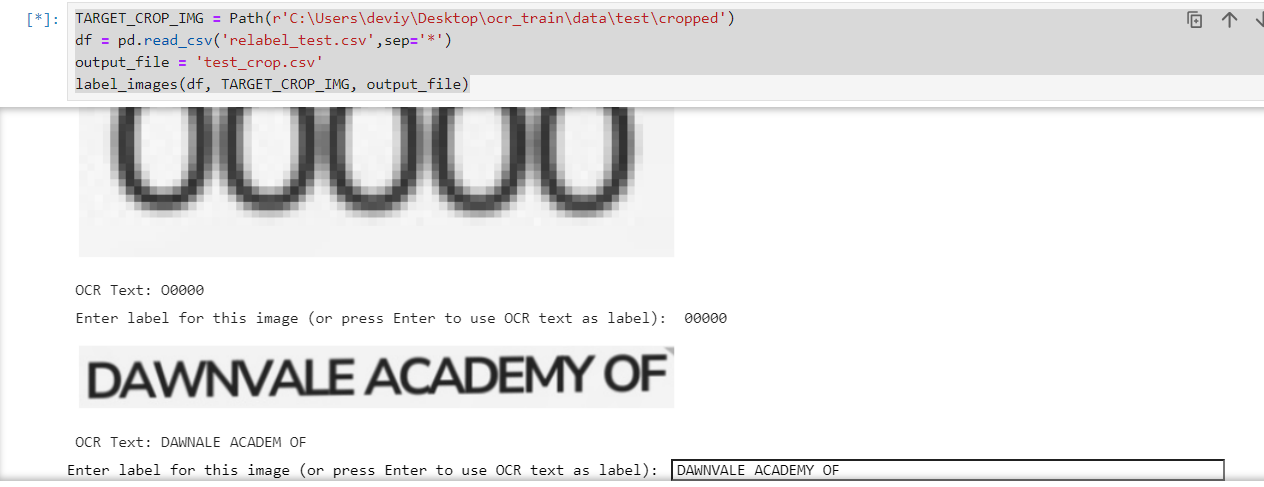
- Utilize the EasyOCR available model, to convert images to text and generate cropped images. Relabel if needed
- Train EasyOCR
- I trained two models. The first model was trained without using a pre-trained model and was limited to 1000 iterations due to resource constraints (CPU only). However, its performance did not meet my expectations. Subsequently, I trained a second model using a pre-trained model, also limited to 1000 iterations. This resulted in a notable improvement in performance, as discussed in next subheader evaluation.
wo pretrained model 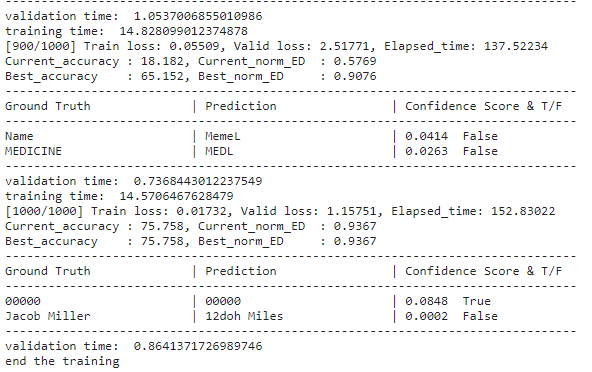
w pretrained model 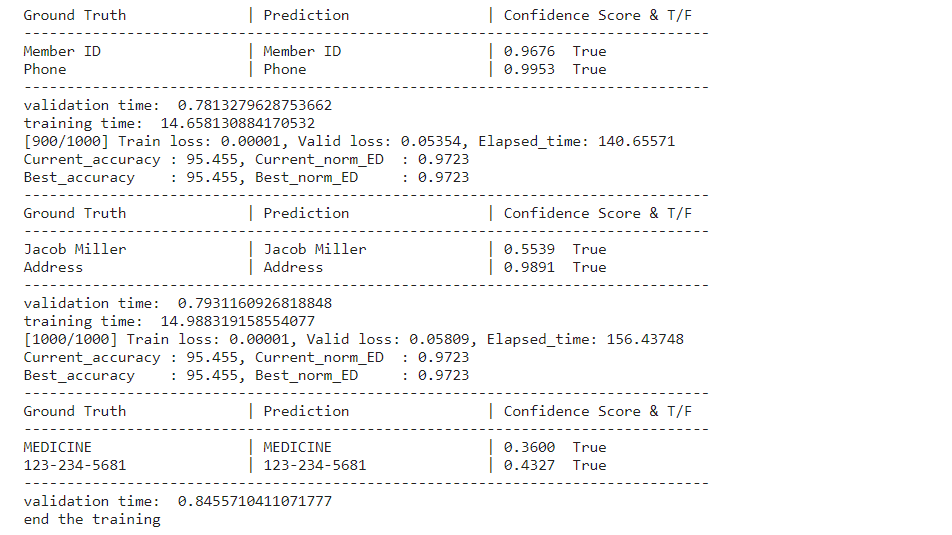
Data Extraction
I made a function that retrieves important information like names, ID numbers, addresses, and phone numbers from scanned ID cards. It double-checks district information by comparing it to master data, finding the closest match from the list, and obtaining the district code based on the selected district name from the master data.
result of test data with v1 model 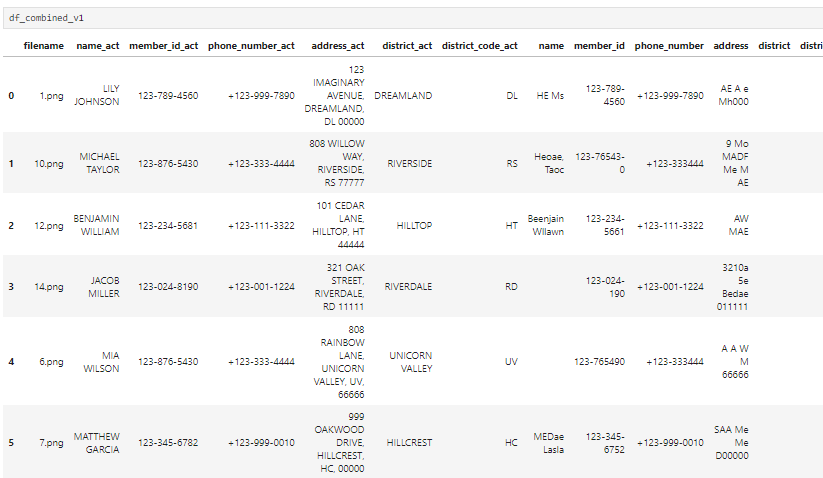
Evaluation
I use 3 metrics:
- CER (Character Error Rate): It measures the percentage of incorrectly recognized characters compared to the total number of characters in the ground truth text. A lower CER indicates better accuracy in recognizing individual characters.
- WER (Word Error Rate): It calculates the percentage of incorrectly recognized words compared to the total number of words in the ground truth text. WER takes into account both substitution errors (wrong words) and insertion/deletion errors (missing or extra words). A lower WER signifies better accuracy in recognizing entire words.
- Accuracy in the context of this project is achieved when the Word Error Rate (WER) equals zero, meaning there are no errors in recognizing words compared to the ground truth.
Performance:
- V1 on test data (normal orientation):
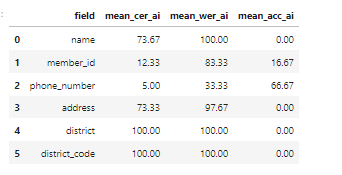
- V2 on test data (normal orientation):
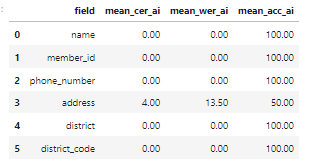
- V2 on rotated test data:
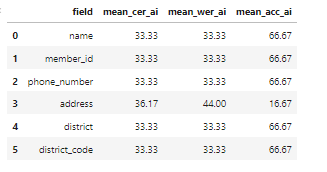
model v2 was chosen
API & Streamlit
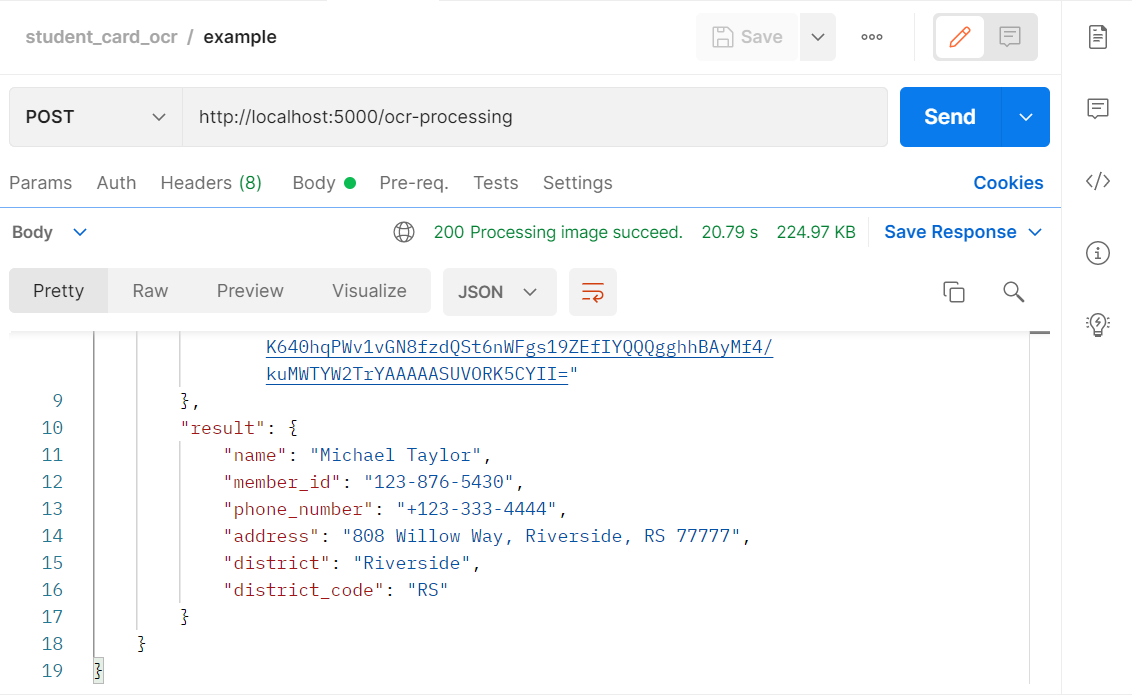

category:
