Credit Scoring
Project Background
Click here to visit github repo
In the modern, digital age, technology is transforming the finance sector by reaching more people. However, it’s a challenge for lenders to judge if customers can pay back loans.
Our project will help Company “X” improve their decision-making. We plan to build a credit scoring model to make loan decisions easier. The model will also set the credit score threshold to help the company reach their target approval rate and default rate.
We’ll use Machine Learning for the credit scoring. The model will score customers based on what we know about past borrowers.
Problem Statement
The upper management of company “X” wants the overall default rate of their portfolio to be below 3% while the approval rate is not less than 70%. Below is the main objective of the project:
- Build a model that predicts whether a loan would be default or not, the result would be the predicted probability of default which indicates a customer is unlikely to pay
- Provide recommendations on the optimal credit score cutoff.
Data: Click here
Some features used were number of credit card, outstanding, credit limit, total year since first card issued, historical data of credit card utilization, payment per bill ratio.
Label Definition: Default (1) and Non-default(0)
Metric used: AUC as it is robust to class imbalance and considers the model’s performance across all possible thresholds
EDA was provided here
Training-test data: 80%:20%
Method
After the initial data cleansing process, I utilized both Logistic Regression (used as our baseline model) and XGBoost for training purposes. To further enhance the performance of our models, I implemented a refinement process using RandomSearchCV.
Performance metrics
Even though it shows that Model #2 has better performance on test dataset, yet Model #4 will be chosen as it has a reduced overfitting. The feature importance of Model #4 is shown below

This bar plot tells us the predictor relative contribution on each of the trees in Model #4 (all features used). delinquency_score, total_retail_usage and total_usage_per_limit are the highest contributors to the model.
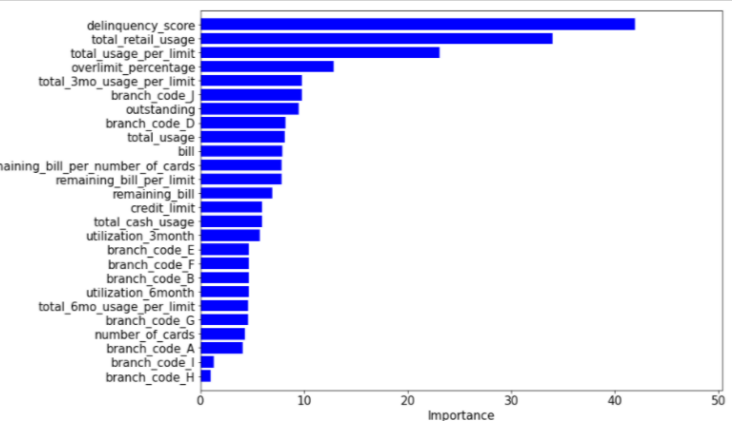
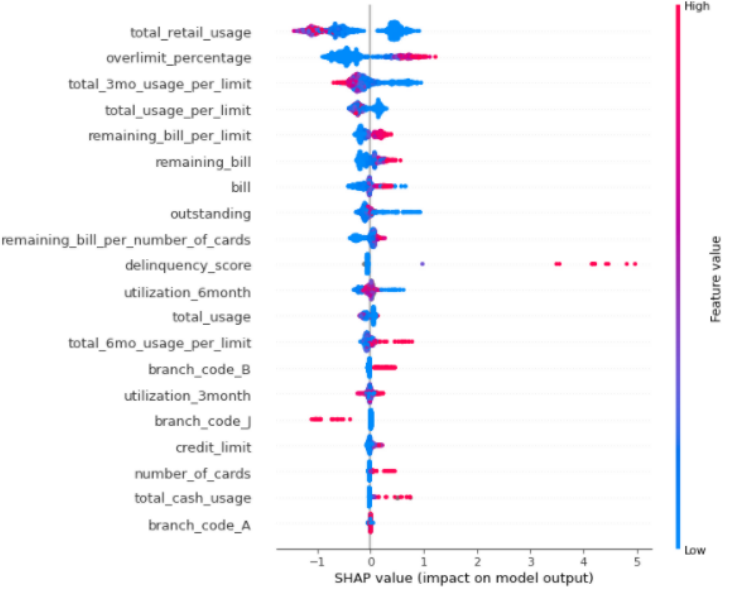
Shap can help us explain the model easier, from the given picture, it shows that lower total_retail_usages, higher overlimit_percentage, lower total_3mo_usage_per_limit can have higher default risk
Inference
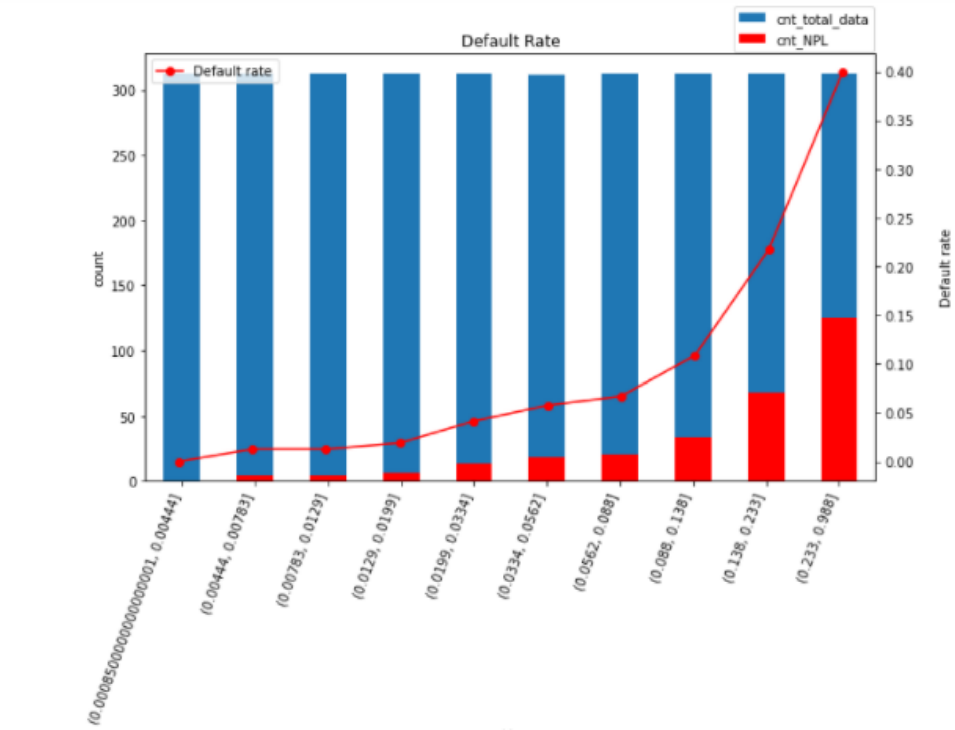
It shows that the higher score that machine learning predict a customer would have no ability to pay back, the more likely our prediction will be correct that the customer will actually not make payments.
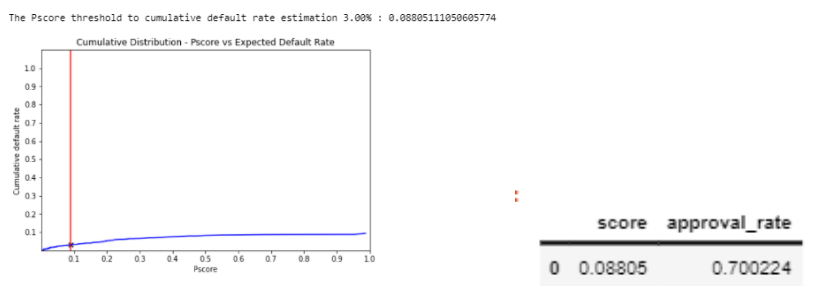
The threshold for achieving default rate below 3% and approval rate higher than 70% = 0.08805
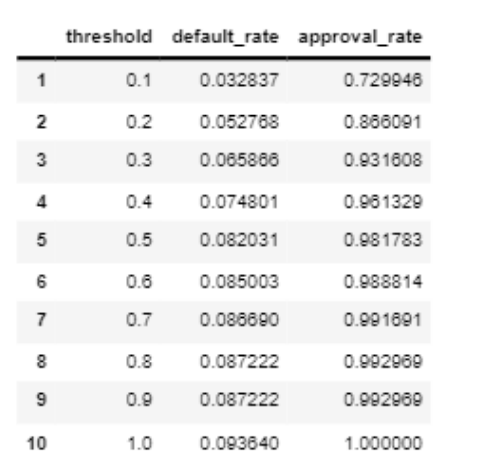
The credit scorecard that can help the nontechnical teams use our model aligning with their plan would be shown below. Example of using the scoring conversion table as follows, approve users with score less than 0.1 then we can get 73% approval rate and 3,2% default rate.
We might need to estimate the profit-loss analysis, for my portfolio, I won’t cover this aspect.
category:
